what are the three major groups of carbohydrates Carbohydrates classification classifications basic following formula source which general notes
Carbohydrates: The Building Blocks of Life Carbohydrates can be defined as organic compounds that are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. These molecules are essential to the functioning of living organisms and play a crucial role in providing the required energy for various bodily functions. There are three primary types of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are single units of sugar molecules, while disaccharides are made up of two monosaccharides joined together. Polysaccharides, on the other hand, are made up of multiple monosaccharides. The primary function of carbohydrates in the human body is to provide energy. When carbohydrates are consumed, they get broken down into smaller molecules, which are then used by cells as fuel for their various processes. Glucose is the primary source of energy for the human body, and it is derived from the breakdown of carbohydrates. In addition to providing energy, carbohydrates also play a crucial role in maintaining healthy digestion. Certain types of carbohydrates, known as dietary fiber, are essential for maintaining healthy bowel movements and preventing constipation. Carbohydrates are also critical to brain function. Glucose is the primary fuel source for the brain, and any fluctuations in blood sugar levels can have a significant impact on cognitive function. It is essential to understand the sources of carbohydrates in your diet, as not all carbohydrates are created equal. Simple carbohydrates, such as those found in candy and sugary drinks, are quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, leading to a rapid rise in blood sugar levels. This sudden spike in blood sugar can lead to a crash in energy levels shortly afterward. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are metabolized more slowly and provide a steady supply of energy over a more extended period. Examples of complex carbohydrates include whole-grain bread, brown rice, and vegetables. To maintain a healthy diet, it is recommended that individuals aim for a balance of both simple and complex carbohydrates. The ratio of carbohydrates to protein and fat may vary depending on an individual’s activity level and overall health goals. In conclusion, carbohydrates are the building blocks of life. These essential molecules play a crucial role in providing energy, maintaining healthy digestion, and supporting brain function. By understanding the different types of carbohydrates and their sources, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their diet and overall health.
If you are searching about Carbohydrates Classification: The basic classification for Quick review you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Carbohydrates Classification: The basic classification for Quick review like All About Carbohydrates - Types, Role, Metabolism & Requirements, Carbohydrate: Structure, Functions and Types | Microbiology Notes and also All About Carbohydrates - Types, Role, Metabolism & Requirements. Read more:
Carbohydrates Classification: The Basic Classification For Quick Review
 www.biochemden.comcarbohydrates classification classifications basic following formula source which general notes
www.biochemden.comcarbohydrates classification classifications basic following formula source which general notes
What Are Carbohydrates, Types, Major Functions. - ChemHow
 chemhoww.blogspot.comcarbohydrates types
chemhoww.blogspot.comcarbohydrates types
All About Carbohydrates - Types, Role, Metabolism & Requirements
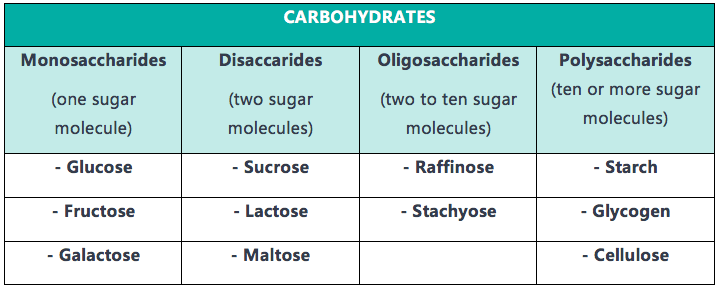 exceednutrition.comcarbohydrates types role carbohydrate categories classified requirements their why they down metabolism into grouped due note these
exceednutrition.comcarbohydrates types role carbohydrate categories classified requirements their why they down metabolism into grouped due note these
Classification Of Carbohydrates With Definition, Types Of Carbohydrates
 byjus.comcarbohydrates classification examples byjus
byjus.comcarbohydrates classification examples byjus
Carbohydrate: Structure, Functions And Types | Microbiology Notes
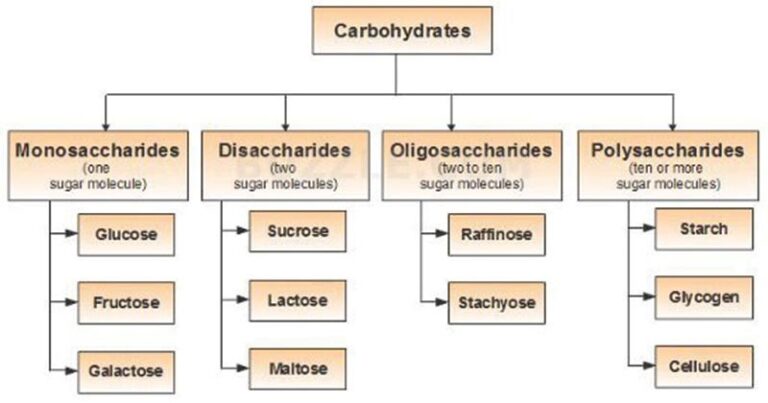 microbiologynotes.orgcarbohydrate carbohydrates classifications saccharides
microbiologynotes.orgcarbohydrate carbohydrates classifications saccharides
All about carbohydrates. Carbohydrates classification examples byjus. Carbohydrates types role carbohydrate categories classified requirements their why they down metabolism into grouped due note these